It feels like a universal truth: battling with WiFi dead zones is just part of modern life. The real solution usually comes down to tackling a few core problems: physical barriers like concrete walls, interference from your neighbours' networks, and simply being too far from your router.
Figuring out which of these is your main issue is always the first step to finally extending your WiFi range for good.
Why Your WiFi Signal Is Weak in the First Place

Before you can really boost your WiFi range, you need to know what's holding it back. I like to think of a router's signal like a lightbulb. The farther away you get, and the more stuff is in the way, the dimmer the light. Your home network works on the exact same principle, but it's dealing with a lot more than just walls.
This guide is your roadmap to getting that seamless connection you're after. We’ll kick things off with some simple, no-cost fixes anyone can do right now, then move into more powerful hardware solutions for those tougher situations. By the end, you'll know exactly how to find and fix your connectivity issues, making unreliable WiFi a distant memory.
Common Culprits Behind Poor Coverage
The reasons for a weak signal almost always fall into a few key buckets. Physical obstructions are the most obvious one. Things like brick, concrete, and even that beautiful solid oak bookshelf can absorb and block radio waves, creating frustrating dead zones. Even something you wouldn't think of, like a big metal fridge or a filing cabinet, can cast a "signal shadow."
Interference from other electronics is another huge factor. Your WiFi signal is sharing the air with a ton of other gadgets, including:
- Neighboring WiFi Networks: If you're in an apartment building or a crowded neighbourhood, you could have dozens of networks all fighting for the same wireless channels. It's like a digital traffic jam that slows everybody down.
- Household Appliances: Common things like microwaves, older cordless phones, and even some baby monitors run on the same 2.4 GHz frequency many WiFi networks use, causing direct signal clashes.
- Bluetooth Devices: While they have less of an impact, a room full of active Bluetooth speakers, headphones, and keyboards can add to the overall network noise.
The Role of Distance and Router Placement
Finally, you can't escape physics. A wireless signal gets weaker the farther it travels. Every foot it moves and every wall it has to push through chips away at its strength. This is precisely why a router stuffed in a basement closet is going to have a hard time giving you a solid connection in a second-floor office.
The single most important thing you can do for whole-home coverage is to put your router in a central spot. Placing it out in the open, and maybe a little elevated, lets the signal radiate outwards and downwards much more effectively. This one move minimises the impact of both distance and obstructions.
Getting a handle on the importance of signal strength in wireless networks is key to fixing these problems. Once you can pinpoint whether your issue is distance, physical barriers, or electronic interference, you can pick the right fix without wasting time and money.
Quick Fixes to Boost Your WiFi Signal Today
Before you go out and buy a new router, you might be surprised by how much you can improve your WiFi signal with a few simple, no-cost adjustments. These are the foundational tweaks that tackle the most common causes of weak coverage. Seriously, you can significantly extend your WiFi range in just a few minutes.
Think of this as a quick tune-up for your existing network to get it running at peak performance.
Relocate Your Router for Maximum Reach
The single most effective change you can make is physically moving your router. So many of us tuck them away in a closet, a cabinet, or a basement corner to keep the blinking lights out of sight. Unfortunately, that's the absolute worst thing you can do for your signal.
Every wall, door, and piece of furniture between the router and your devices acts as a barrier, weakening the connection.
Imagine your router's signal radiating outwards like ripples in a pond. To cover the whole pond, you have to drop the pebble right in the center. Your home network works the exact same way.
For the best possible coverage, place your router in a central, open, and elevated location.
- In a two-story house: A high shelf on the first floor is often the sweet spot. This lets the signal travel outwards to cover the main level and upwards to reach the second floor.
- In a single-story home or apartment: Find a central spot in your main living area or hallway. Putting it on a bookshelf or a small table gets it off the floor and above obstructions like sofas and coffee tables.
Definitely avoid placing it near large metal objects like refrigerators, thick concrete walls, or even aquariums—water is surprisingly good at absorbing WiFi signals. This one simple move can solve a ton of dead zone problems without costing you a dime.
For more detailed strategies on router placement and other enhancements, check out our comprehensive guide on how to improve home WiFi.
Optimize Your WiFi Channels and Frequency Bands
Once your router is in the perfect spot, the next step is fine-tuning its broadcast settings. Most modern routers are dual-band, meaning they broadcast on two different frequencies: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Knowing the difference is key to getting the most out of your network.
The 2.4 GHz band uses longer radio waves, which are much better at penetrating solid objects like walls. This gives it a longer range. The downside? It's a crowded frequency, competing with neighbors' WiFi, microwaves, cordless phones, and even Bluetooth speakers.
The 5 GHz band uses shorter waves, letting it transmit data much, much faster. The catch is that these shorter waves don't travel as far and are more easily blocked by physical obstacles.
Pro Tip: Think of 2.4 GHz as a reliable sedan that can handle bumpy roads (walls) over long distances. The 5 GHz band is more like a sports car—incredibly fast on a clear highway but struggles off-road.
To manage this, try separating your networks. You can give them distinct names in your router settings (like "MyHomeWiFi_2.4" and "MyHomeWiFi_5"). Connect devices that are far from the router to the 2.4 GHz network. For high-performance devices that are closer, like your streaming TV or gaming console, connect them to the 5 GHz network for a serious speed boost.
Choosing Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi Bands
Use this quick guide to decide which WiFi band is best for your devices based on their location and your need for speed versus range.
| Characteristic | 2.4 GHz Band | 5 GHz Band |
|---|---|---|
| Range | Longer range; better at penetrating walls and floors. | Shorter range; struggles more with physical obstructions. |
| Speed | Slower maximum speeds. | Significantly faster maximum speeds. |
| Interference | More prone to interference from other WiFi networks and common household devices. | Less prone to interference; has more available channels. |
| Best For | Smart home devices, browsing on devices far from the router, general use. | 4K streaming, online gaming, large file transfers on devices close to the router. |
Choosing the right band for each device is a simple way to make sure everything on your network runs as smoothly as possible.
Keep Your Router's Firmware Updated
Finally, one of the easiest yet most overlooked fixes is a firmware update. Firmware is the software that runs your router, and manufacturers regularly release updates to improve performance, patch security holes, and sometimes even add new features.
Running on outdated firmware can lead to slower speeds, dropped connections, and an unstable network. While most modern routers update automatically, it’s a good habit to log into your router's admin panel every few months to manually check.
The whole process usually just takes a few minutes and can make a noticeable difference in your signal strength and reliability. These quick fixes are the foundation of a healthy home network and your first line of defense against frustrating WiFi dead zones.
Choosing the Right Hardware: WiFi Extenders vs. Mesh Systems
When you've tried all the free fixes and still find yourself stuck with stubborn dead zones, it’s time to look at a hardware upgrade. This is where most people hit a fork in the road, trying to figure out the best way to extend their WiFi range. The two main options you'll see are traditional WiFi extenders and modern mesh WiFi systems.
Let's break down the core difference. A WiFi extender, which you might also hear called a repeater, basically acts like a relay. It grabs the existing signal from your main router, gives it a boost, and rebroadcasts it to cover a wider area. Think of it as a simple megaphone for your WiFi.
A mesh WiFi system, on the other hand, is a complete overhaul. It replaces your current router with a team of smart, interconnected "nodes" that you place around your home. These nodes all talk to each other to blanket your entire space in a single, unified network.
The Case for WiFi Extenders
For a lot of people, a simple WiFi extender is a good first step. They’re cheap and they get a specific job done: pushing your signal just a little farther to solve a single problem area, like a dead spot on the back patio or in an upstairs bedroom.
The biggest draws for an extender are its low cost and simplicity. You can usually grab a decent one for less than $50, plug it into an outlet somewhere between your router and the dead zone, and have it running in minutes with a simple app.
But that convenience comes with some serious trade-offs you need to know about.
- Bandwidth Reduction: Most extenders have to use half their bandwidth to receive the signal from your router and the other half to broadcast it. This can slash your potential internet speed in half for any device connected to that extender.
- A Separate Network: An extender creates a brand-new network, usually with "_EXT" tacked onto your original WiFi name. This means your phone won't automatically switch as you walk through the house. You have to manually disconnect from your main network and connect to the extender to get that stronger signal, which can be a real pain.
Before you jump to buying new hardware, make sure you've covered the basics. This flowchart runs through some of the initial, no-cost fixes you should always try first.
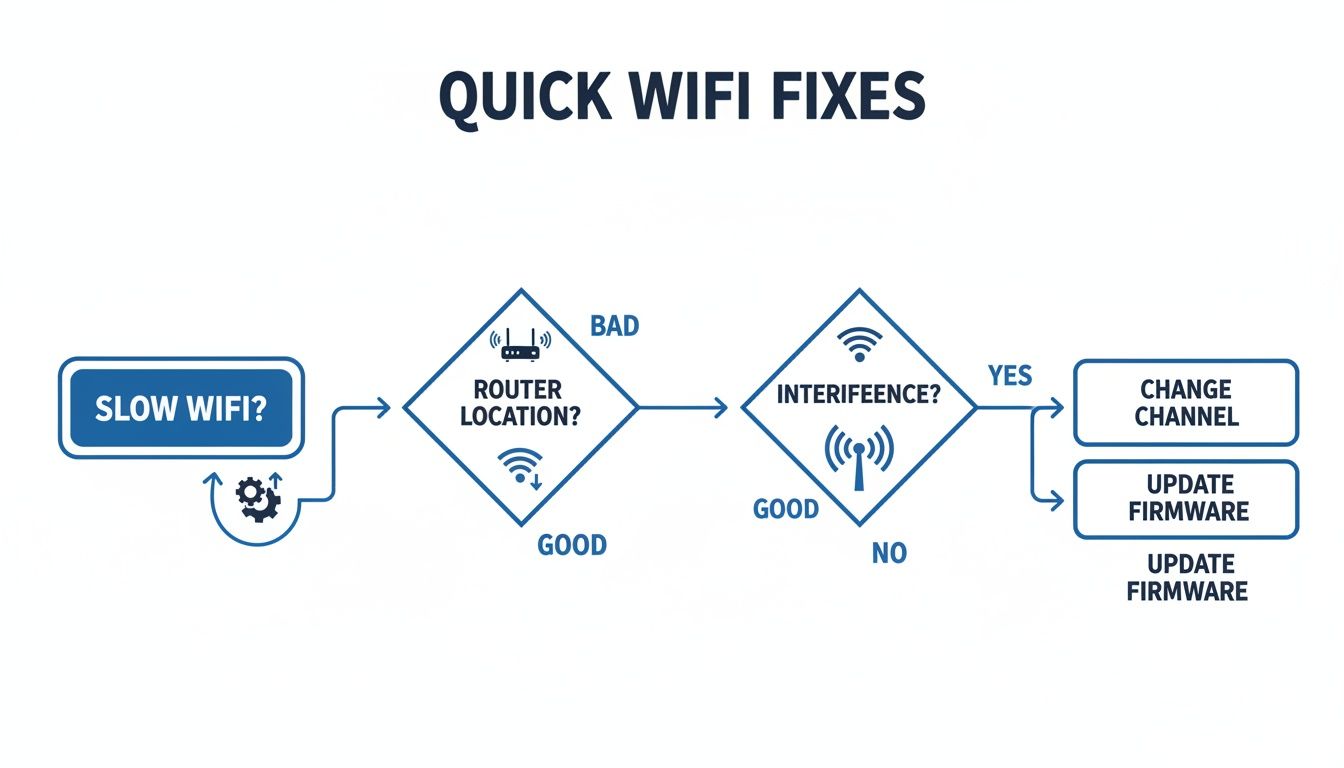
As you can see, simple things like moving your router or updating its channels are foundational steps that can often solve common connection headaches without costing a dime.
The Superiority of Mesh WiFi Systems
If you're dealing with a larger home, multiple floors, or a house full of devices, a mesh WiFi system is easily the more powerful and elegant solution. The upfront cost is higher, no doubt, but the performance payoff is massive and it solves the core problems that extenders create.
A mesh system creates one seamless network with a single name and password. As you move from room to room, your devices intelligently and automatically hop to the nearest node, making sure you always have the strongest signal without any frustrating drop-offs or manual switching. It’s the best way to get consistent speeds absolutely everywhere.
Mesh systems are built from the ground up for whole-home coverage. Instead of just patching dead zones, they eliminate them entirely, delivering a strong, fast connection from the basement all the way to the attic.
The market for these devices is growing fast. While Wi-Fi extenders held a majority of the market share back in 2020, the repeater segment is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 11.4%. You can read the full research about the Wi-Fi range extender market to see how consumer demand is shifting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
So, which one is right for you? It really boils down to the size of your problem and what kind of performance you expect. This table should help you quickly compare the two.
| Feature | WiFi Extender | Mesh WiFi System |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Small, specific dead zones in smaller homes or apartments. | Medium to large homes, multi-story layouts, and complex floor plans. |
| Performance | Can cut speeds by up to 50%. | Delivers consistent, high speeds across your entire home. |
| Network | Creates a separate network requiring manual switching. | Creates a single, unified network for seamless roaming. |
| Cost | Low initial cost, typically $30-$100. | Higher initial cost, typically $150-$500+. |
| Setup | Simple plug-and-play setup. | Slightly more involved but still user-friendly. |
For anyone ready to invest in a truly reliable, high-performance network, a mesh system is the clear winner. If you want a closer look at what it takes to get one going, check out our guide on how to set up mesh WiFi. Choosing the right hardware is the key to finally extending your WiFi range and getting rid of those frustrating dead zones for good.
Advanced Strategies for Power Users and Demanding Homes

For remote workers, serious gamers, and homes overflowing with smart devices, the standard fixes just don't cut it. When your daily life hinges on flawless, high-speed connectivity, it's time to dig into some pro-level strategies that are all about peak performance. These tactics go beyond just covering dead zones; they're about optimizing every bit of data for the most demanding tasks.
Hardwire Your Mesh with Ethernet Backhaul
If you've already set up a mesh WiFi system but still crave absolute stability, using a wired Ethernet backhaul is a game-changer. This just means you're physically connecting your mesh nodes to each other with Ethernet cables, often routed through walls, a basement, or an attic.
What's the point? You're essentially creating a private, high-speed highway for your mesh nodes to talk to each other. This frees up the wireless bands completely, dedicating 100% of their capacity to your laptops, phones, and smart TVs. The result is a massive speed boost and a rock-solid connection at every single node—perfect for transferring huge files or staying crystal-clear on that crucial video call.
Prioritize Your Most Important Traffic
Another powerful tool hiding in most modern routers is Quality of Service (QoS). Think of QoS as the bouncer for your home network. It lets you tell your router which devices or applications get VIP treatment, ensuring they always have the bandwidth they need.
For instance, you can set your work laptop and your gaming console as high-priority devices. When the network gets congested—say, when someone starts streaming 4K in the living room while another person is downloading a huge file—QoS automatically funnels more bandwidth to your priority gadgets. No more stuttering on your Zoom calls or lagging out in the middle of a game.
Implementing QoS is like creating a VIP lane on your internet connection. It ensures that the data packets from your most important activities—whether that's a video conference or an online match—always get to the front of the line, drastically reducing frustrating lag and interruptions.
The technology for extending WiFi has come a long way. Old-school extenders were notorious for cutting your speeds in half, but modern solutions using dual-band, tri-band, and Wi-Fi 6E have completely changed the game. The move to Wi-Fi 6E and the 6 GHz spectrum, in particular, has opened up new, uncongested channels, boosting speed and slashing interference. You can see more on the evolving Wi-Fi range extender market on Allied Market Research.
As these standards advance, it pays to know what you're buying. We break down the key differences in our guide to WiFi 6 vs WiFi 7 and its impact on your home office.
Upgrade Your Router and Antennas
If your router is more than a few years old, it’s probably the biggest bottleneck on your network. Stepping up to a modern router, especially one supporting newer standards like Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E, can deliver a night-and-day difference in both speed and range. These new models are built from the ground up to juggle dozens of devices without breaking a sweat.
Many high-performance routers also come with detachable antennas. This is a huge plus. You can swap out the stock antennas for more powerful, high-gain models designed to focus the signal where you need it most.
- Omni-directional antennas: These broadcast a signal in all directions, just like the ones your router came with.
- Directional antennas: These focus the signal into a tight beam, perfect for punching through walls to reach a backyard office or a detached garage.
For truly challenging layouts—like a large home with brick walls or a small business with lots of interference—the ultimate fix is a professional site survey. A technician uses specialized gear to map out signal strength, pinpoint interference sources, and design a custom network with the perfect hardware and placement for 100% coverage.
When Your Internet Plan Is the Real Problem
So you’ve tried every trick in the book. You’ve moved the router, tweaked the settings, and maybe even upgraded your hardware, but your connection is still frustratingly slow. What gives?
Sometimes, the problem isn't your Wi-Fi at all. The real bottleneck can be the internet service coming into your home in the first place. If your speeds are crawling even when you’re standing right next to the router, that’s a huge red flag. Your internet plan itself is likely holding you back.
Think of it this way: no amount of fancy Wi-Fi gear can create speed that isn’t there to begin with. Trying to boost a slow, unreliable signal just gives you a wider area of poor performance. It’s like trying to fill a swimming pool with a dripping faucet—you can add more hoses (extenders), but the fundamental problem is the weak water pressure from the source.
Identifying a Service Bottleneck
Before you point the finger at your Wi-Fi, it’s worth taking a step back. Getting a handle on understanding broader technological issues, including unreliable internet, can help you zero in on the true source of your headaches.
Here’s a simple test that cuts right to the chase: plug a laptop directly into your modem using an Ethernet cable and run a speed test.
If that wired speed is way below what you’re paying for, your plan is almost certainly the culprit. This is especially common with older technologies like DSL or cable, which just can't keep up with the demands of a modern, connected home. Symmetrical speeds—where your upload and download are equally fast—are no longer a luxury; they're essential for how we use the internet today.
A robust, high-speed fiber connection provides a powerful and stable foundation that your home network can build upon. It ensures that the internet entering your home has enough capacity to support all your devices, from 4K streaming to critical work video calls, without compromise.
This growing need for solid home connectivity is why the home networking market has exploded. The global demand for Wi-Fi range extenders is a clear sign of how many people are fighting for reliable wireless access. For service providers like Premier Broadband, this trend highlights a real opportunity to offer managed Wi-Fi solutions that go beyond just a basic connection, especially for the growing number of people working from home.
When to Upgrade Your Internet Plan
So, how do you know it’s officially time to make the switch? If you've recently loaded up your home with more smart devices, have more family members online, or have started working from home, your old plan is probably struggling to keep up.
Look out for these classic signs that you’ve outgrown your current service:
- Constant Buffering: Your movie night is constantly interrupted by that dreaded spinning wheel, especially during peak evening hours. This means your connection just doesn't have the bandwidth.
- Lag During Gaming or Video Calls: Activities that need a fast, responsive connection, like online gaming or a Zoom meeting, are the first to suffer. If you’re experiencing lag spikes or dropped calls, your connection is to blame.
- Painfully Slow Uploads: It takes forever to upload a large work file or back up your photos to the cloud. This is a classic symptom of plans with weak upload speeds, a common limitation of non-fiber connections.
Sure, a quick power cycle—unplugging your modem and router for 60 seconds—can sometimes fix a temporary glitch. But if these problems are part of your daily routine, it's a clear signal that your internet plan is the real problem. Upgrading to a modern fiber connection is the most definitive step you can take to ensure your entire network performs at its absolute best.
Common Questions About Extending Your WiFi Range
After diving into all the ways to boost your WiFi signal, a few key questions always seem to come up. Let's tackle them head-on so you can clear up any confusion and pick the absolute best solution for your home.
Do WiFi Extenders Really Slow Down Your Internet?
In a word, yes. Most traditional WiFi extenders will cut your internet speed. Think of it this way: the extender has to listen to the signal from your router and then rebroadcast it. That process of listening and talking back to the router uses up about 50% of its available bandwidth.
So, any device you connect to the extender is only getting what’s left over. This is why they’re really only good for low-stakes situations, like connecting a smart plug in the garage or just casually browsing on a tablet out on the patio. Try to stream 4K video or game on an extender, and you’re going to feel that bottleneck in a big way.
What’s the Real Difference Between an Extender and Mesh WiFi?
The biggest difference you'll actually notice day-to-day is having one seamless network versus two clunky ones. A WiFi extender creates a totally separate network (you'll see something like "MyHomeWiFi_EXT"). Your devices won't automatically switch between your main router and the extender, which means you have to do it manually as you move around. It gets old, fast.
A mesh system, on the other hand, creates a single, unified network. As you walk from the living room to the bedroom, your phone or laptop gets handed off to the nearest mesh node automatically. You won't notice a thing.
Here's a good analogy: An extender is like adding a second, separate radio station to cover a weak area. A mesh system is like upgrading to a whole network of synchronized broadcast towers that all play the same station perfectly, giving you flawless reception everywhere you go.
How Many Extenders or Mesh Nodes Do I Actually Need?
Getting the number right is crucial. Too few and you'll still have dead zones; too many and you're just wasting money and potentially creating more interference. It all comes down to your home's size, layout, and what the walls are made of.
- For WiFi Extenders: You almost always just need one. Their job is to patch a single, specific dead zone. Trying to daisy-chain multiple extenders is a recipe for a messy, unreliable network.
- For Mesh Systems: A good rule of thumb is one node for every 1,500 to 2,000 square feet. So, a standard 3,000-square-foot, two-story house will probably get perfect coverage from a three-pack (the main router and two satellite nodes). If you have thick brick walls or a really funky layout, you might need an extra node to punch the signal through.
Can I Use a WiFi Extender with My Mesh System?
You can, but you really shouldn't. It's like putting cheap tires on a sports car—you're completely undermining the performance you paid for. Adding a traditional extender to a slick mesh system just reintroduces that separate, clumsy network and completely bypasses the smart routing that makes mesh so great.
If your mesh system has a weak spot, the only real solution is to add another compatible node from the same company. It will slide right into your existing network, keeping everything seamless and running at peak performance.
Ready to leave dead zones and buffering behind for good? Premier Broadband delivers ultra-fast, reliable connectivity through our 100% fiber network. Get the powerful foundation you need for flawless whole-home WiFi today. Explore our high-speed internet plans.

