If you’ve ever been on a VoIP call that sounds choppy, robotic, or just cuts out entirely, you’ve experienced a bandwidth problem firsthand. It’s not an issue with your phone service; it’s a problem with the digital highway it runs on. For conversations that are crystal-clear, you need a connection where both upload and download speeds matter equally.
Why Bandwidth Is The Key To Clear VoIP Calls
Think of your internet connection like a water pipe. If the pipe is too narrow or clogged, all you get is a sputtering trickle of water. It's the same with VoIP. When you don't have enough bandwidth, the audio becomes a garbled, unreliable mess. That's because VoIP technology chops your voice into tiny digital data packets and sends them over the internet. For the person on the other end to hear you clearly, those packets need a wide-open path to arrive on time and in the right order.
When that path gets congested, a few things can quickly ruin a call:
- Jitter: This is when data packets arrive out of sequence. It’s what makes voices sound robotic and distorted.
- Latency: You know that awkward delay between when you speak and when the other person hears you? That’s latency, and it makes natural conversation nearly impossible.
- Packet Loss: Sometimes, data packets get lost in transit completely. This leads to gaps in the audio or, even worse, a completely dropped call.
The Two-Way Street of Communication
Unlike streaming a movie where you're just downloading data, a phone call is a real-time, two-way conversation. You're sending and receiving data at the exact same time. This is why having a strong upload speed is just as crucial as download speed for VoIP. If your upload is slow, your voice will sound choppy and broken to the other person, even if you can hear them perfectly. You can learn more about this in our guide to what makes a good upload speed.
This need for a solid, two-way data connection is what’s fueling the massive growth in the VoIP industry. The global VoIP market was valued at a huge $132.47 billion in 2023 and is expected to rocket to $326.27 billion by 2032. This shift shows just how many homes and businesses are moving away from old-school phone lines to more flexible, internet-based phone systems.
At the end of the day, the principle is simple: your VoIP system is only as reliable as the internet connection supporting it. Getting the right amount of bandwidth isn't just a tech spec—it's how you ensure professional, clear, and dependable communication.
Ultimately, securing the right bandwidth for VoIP is all about making sure your digital "pipe" is wide enough to handle your voice traffic without a hitch.
Understanding Codecs: The Language Of VoIP
Every time you make a VoIP call, there's a fascinating bit of technology working behind the scenes called a codec. You can think of a codec (which is short for coder-decoder) as a digital translator for your voice. It takes the sound of you speaking, compresses it into tiny digital packets for its journey across the internet, and then quickly unpacks it back into clear audio for the person you're talking to.
The specific codec your VoIP system uses is a huge factor in how much internet bandwidth you'll need. Why? Because different codecs compress audio differently, creating a classic trade-off: pristine call quality versus lower data use. It’s like saving a photo. A huge, uncompressed file looks amazing but takes up a lot of space, while a smaller, compressed JPEG is much more efficient but might lose a tiny bit of detail.
And the demand for that efficient, high-quality service is exploding.
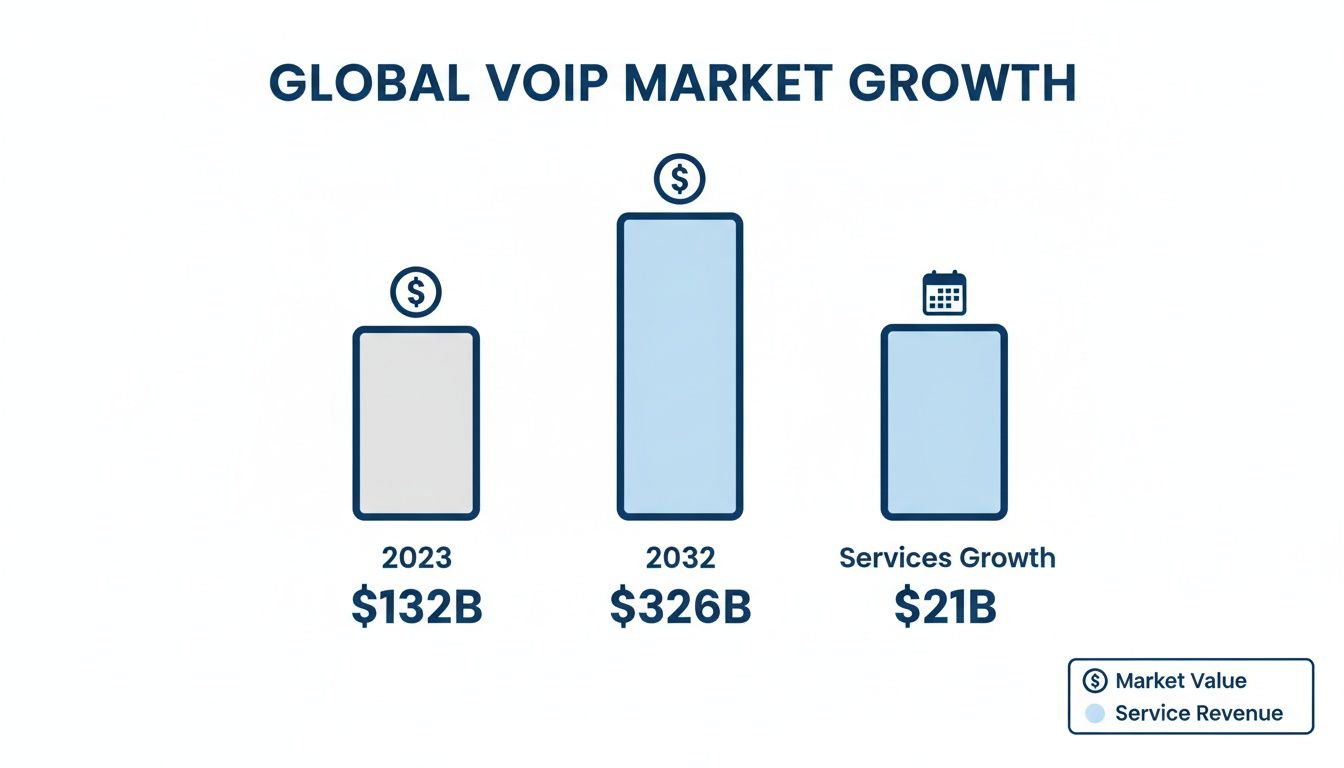
As this chart shows, the VoIP market is on a massive growth trajectory, projected to jump from $132 billion to over $326 billion by 2032. This surge makes it more important than ever for homes and businesses to get a handle on the technical side of their phone service.
High Fidelity vs. High Efficiency
To see this quality-versus-efficiency balancing act in action, let’s look at two of the most popular codecs used today. Each one is built for a different priority, which directly changes how much bandwidth you consume.
- G.711: The Quality King. This is the gold standard for crystal-clear audio. It uses very little compression, giving you a rich sound that’s just like an old-school landline. That premium quality comes at a cost, though—it uses around 87 Kbps of bandwidth for every call.
- G.729: The Efficiency Expert. On the other end of the spectrum, G.729 is all about saving bandwidth. It uses smart compression to shrink the audio data down, needing only about 32 Kbps per call. This makes it perfect for situations where your internet connection might be limited, though you do sacrifice a bit of that top-end audio fidelity.
To really get a feel for the options, here’s a quick look at some common codecs and how they stack up.
Common VoIP Codecs and Their Bandwidth Needs
This table breaks down the most popular codecs, showing the give-and-take between audio quality and the internet speed required to support it.
| Codec | Bandwidth (without overhead) | Total Bandwidth (with overhead) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| G.711 | 64 Kbps | ~87 Kbps | Maximum audio quality, equivalent to traditional phone lines. |
| G.729 | 8 Kbps | ~32 Kbps | Low-bandwidth environments where efficiency is key. |
| G.722 | 64 Kbps | ~87 Kbps | High-definition (HD) voice calls with a wider audio range. |
| Opus | 6-510 Kbps (Variable) | ~20-523 Kbps (Variable) | Modern applications; dynamically adjusts for quality vs. network conditions. |
As you can see, the choice of codec directly impacts your bandwidth budget, making it a critical factor in designing your VoIP setup. If you want to dig deeper into how the core technology works, our guide on how a VoIP phone works is a great place to start.
The Hidden Cost Of Network Overhead
But the codec's data rate is just one piece of the puzzle. Every single packet of voice data also carries extra information called network overhead. Think of it like the shipping label, box, and packing tape on a package you send. This overhead contains routing information (IP, UDP, and RTP headers) that tells the packets where to go and how to reassemble in the right order.
This overhead is a fixed addition to every packet, tacking on an extra 16 to 24 Kbps to the codec's bandwidth. It's a small but critical detail that many people forget when calculating their actual needs.
This means a call using the high-quality G.711 codec doesn't just use 87 Kbps—it actually eats up closer to 100 Kbps once you add in the overhead. That difference becomes massive when you start planning for multiple calls happening at the same time. While a basic call might need just 100 Kbps, modern business demands are pushing that number higher. Enterprise-level calls, especially with AI-driven features, can now require 1-2 Mbps per line.
This is exactly where Premier Broadband's symmetrical fiber internet shines, giving small businesses the power to run hosted VoIP systems and AI cameras without worrying about performance killers like jitter and lag.
How To Calculate Your Total VoIP Bandwidth Needs
Now that we've covered how codecs and network overhead add up, let's put it all together. Figuring out your total bandwidth for VoIP isn't some complex technical puzzle; it's about making sure your phones work flawlessly when you need them most. The good news is, it boils down to a pretty simple formula.
At its heart, the math looks like this:
(Bandwidth Per Call) x (Maximum Simultaneous Calls) = Total VoIP Bandwidth Needed
This calculation gives you a solid baseline for the amount of bandwidth you need to set aside just for your voice traffic. Let's walk through each piece so you can figure this out for your own setup.
Step 1: Figure Out Your Bandwidth Per Call
First things first, you need to know how much data a single call uses. As we discussed, this number comes from the codec your VoIP provider uses, plus a little extra for network overhead. A very common, high-quality codec like G.711 needs about 87 Kbps.
To be safe and make the math easy, we can round that up to 100 Kbps (or 0.1 Mbps) per call. This is a great, conservative number to use for planning. It gives you plenty of buffer for crystal-clear audio and all the data routing that happens in the background.
Step 2: Estimate Your Maximum Simultaneous Calls
This is the most important part of the equation, and it’s all about planning for your busiest moment, not your average one. You need to estimate the absolute peak number of calls that could be happening at the exact same time. We call this peak concurrent calls.
Why plan for the peak? Simple. Your phone system is most critical when things are hectic. If you only plan for a quiet Tuesday morning, your call quality will tank during a big sales push or when customer service is flooded with calls.
Here are a few rules of thumb to get your number:
- For Small Businesses: A good starting point is to assume one out of every three or four employees might be on a call at the same time during peak hours. So for an office of 10 people, planning for 3 to 4 concurrent calls is a smart move.
- For Call Centers: This is a different ballgame. You'll need to plan for a much higher percentage, likely 75% to 90% of your agents on calls simultaneously.
- For Home Offices: If you're a solo remote worker, you usually only need to account for one call. But if two people are working from home, it's wise to plan for two simultaneous calls.
Once you have that number, you're ready to plug it into the formula. For example, let's say a small business expects a peak of 10 simultaneous calls:
0.1 Mbps (per call) x 10 (simultaneous calls) = 1.0 Mbps
This means you need to have 1.0 Mbps of dedicated upload and download speed available just for your VoIP system. The easiest way to see where you stand is to run a quick VoIP bandwidth test to check your current connection's performance.
Step 3: Remember, Upload Speed is Just as Important
It’s a classic mistake to only look at download speed. A VoIP call is a live, two-way street—data is constantly flowing in both directions. Your voice is sent out using your upload bandwidth, while you hear the other person through your download bandwidth.
This is exactly why symmetrical speeds, where your upload and download speeds are identical, are the gold standard for VoIP. If your upload speed is lagging way behind your download (a common headache with older cable internet), people on the other end of the line will hear garbled, choppy audio from you, even if they sound perfect.
So when you calculate that you need 1.0 Mbps for VoIP, that means you truly need 1.0 Mbps of upload AND 1.0 Mbps of download capacity free at all times. This is where fiber internet from providers like Premier Broadband really shines, delivering the kind of symmetrical speeds that make voice and video calls work perfectly.
Moving Beyond Speed To Ensure Call Quality
Figuring out the right amount of bandwidth for your VoIP system is a great first step, but it’s really only half the battle. Having a big enough digital highway is essential, but the condition of that highway is what makes the difference between a crystal-clear call and a garbled, frustrating mess. Raw speed alone just doesn't cut it.

Think of it like this: you can have an eight-lane superhighway, but if it's riddled with potholes and prone to sudden traffic jams, nobody's getting where they need to go on time. The same exact principle applies to your internet connection. A few common "network health" issues can completely derail your calls, even if you have plenty of speed to spare.
The Hidden Culprits Behind Poor Calls
When a VoIP call goes bad, it's almost always one of three culprits causing the trouble. If you know what they are, you can spot and fix the problems before they drive you crazy.
Latency (Delay): This is the time it takes for a voice packet to travel from your phone to the person you're talking to. High latency is what causes that awkward, noticeable pause in a conversation where you end up talking over each other. For a natural-sounding call, you need latency to be under 150 milliseconds.
Jitter (Inconsistency): Jitter happens when those little voice packets arrive out of order. Your VoIP system then has to scramble to put the conversation back together correctly, which often leads to robotic or choppy audio. If you want to dive deeper, we have a whole guide on what jitter is in networking and how to fix it.
Packet Loss (Disappearance): Sometimes, voice packets just get lost on the way and never arrive at their destination. Even a tiny amount of packet loss—as little as 1-2%—can create gaps in the audio, making it sound like entire words or parts of sentences are missing.
These problems pop up most often on busy networks where every type of data is fighting for the same resources without any rules of the road.
Creating a VIP Lane with Quality of Service
So, how do you shield your calls from these issues? The most powerful tool in your arsenal is Quality of Service (QoS). Think of QoS as a dedicated traffic cop for your internet connection. It's a network management feature that lets you prioritize certain types of data over others.
By setting up QoS, you can create a dedicated "fast lane" just for your VoIP traffic. You’re essentially telling your router that voice packets are the most important data on the network and must always get to go first.
With QoS enabled, a massive file download, a 4K video stream, or a big software update won't interfere with your phone calls. Your voice data gets the VIP treatment, bypassing any potential network traffic jams.
This kind of control is becoming non-negotiable as more homes and businesses switch to VoIP. In fact, the global user base is expected to blow past 3 billion by 2024, with small and medium-sized businesses driving much of that growth. These companies are adopting cloud-based systems for the same kind of advanced features offered by providers like Premier Broadband.
For businesses dealing with a lot of network traffic, a Managed Ethernet Switch can be a game-changer for enforcing these QoS rules and ensuring your calls are always the top priority. After you’ve calculated your bandwidth needs, implementing QoS is the single most important thing you can do to get consistently reliable, professional-sounding calls.
Real-World Bandwidth Scenarios For Homes and Businesses

Theory and formulas are a great start, but let's put them to the test in the real world. To make the concept of bandwidth for VoIP truly click, we’ll walk through two common scenarios: a modern home office and a growing small business.
These practical examples will show you exactly how to think about your own needs, helping you choose the right internet plan without overpaying for bandwidth you don't need or, even worse, coming up short when it matters most.
Scenario 1: The Modern Home Office
Let’s look at Alex, a consultant who works entirely from home. A typical day for Alex involves a steady stream of VoIP calls, team video conferences, and heavy use of cloud-based tools. When the workday is done, the rest of the household loves to stream movies and play online games. Alex needs an internet plan that can juggle everything seamlessly.
Step 1: Pinpoint All Internet Activities
First, we need a list of everything competing for that internet connection:
- VoIP Calls: Alex is the only one on business calls, so we'll plan for 1 simultaneous call.
- Video Conferencing: Frequent HD video calls are a major bandwidth hog.
- Cloud Applications: Tools like Dropbox and Salesforce are always syncing in the background.
- Household Use: After-hours entertainment includes 4K video streaming and online gaming.
Step 2: Calculate the Required Bandwidth
Using our safe estimate of 100 Kbps (0.1 Mbps) per VoIP call, the math is simple:
0.1 Mbps per call x 1 call = 0.1 Mbpsset aside for voice.
But that tiny fraction is just for the phone call itself. A single high-definition video call can easily chew up 3-4 Mbps of both your download and upload speed. To keep everything running smoothly, Alex needs a buffer of at least 25% on top of whatever the peak usage might be.
Step 3: Determine the Ideal Plan
For Alex, symmetrical speeds are a must-have. All those video meetings demand a powerful and stable upload connection.
A classic mistake for remote workers is getting a plan with blazing-fast download speeds but weak upload speeds. This leads to them hearing everyone else perfectly, while their own voice and video come across as a choppy, unreliable mess.
For this kind of setup, a symmetrical fiber plan like Premier Broadband's 100 Mbps service is the perfect fit. It provides plenty of headroom for crystal-clear VoIP and video calls, even if other people in the house are streaming or gaming at the same time.
Scenario 2: The Growing Small Business
Now, picture a small marketing agency with 10 employees. The office is a busy hub of client calls, constant uploading and downloading of large design files, and a couple of security cameras streaming video feeds. The owner needs a phone system that’s rock-solid today and ready for future growth.
This is an incredibly common situation. The global VoIP services market exploded to roughly $112.9 billion in 2023 and is expected to climb to $179.6 billion by 2026. This boom is powered by small businesses moving away from old-school phone lines to more flexible and affordable cloud communications. You can read more about the VoIP market's impressive growth on sheerbit.com.
Step 1: Estimate Peak Concurrent Calls
With 10 people in the office, you have to plan for the busiest times. A good rule of thumb is the one-in-three rule, which means we should prepare for a peak of 4 simultaneous calls.
Step 2: Calculate the Required VoIP Bandwidth
0.1 Mbps per call x 4 calls = 0.4 Mbps
This is the absolute minimum amount of bandwidth that must be exclusively reserved for voice traffic to prevent call quality issues.
Step 3: Account for Other Business Needs
Of course, the agency's internet usage goes way beyond phone calls:
- Cloud Software: The creative team is constantly moving large files to and from the cloud.
- Security Cameras: Two HD cameras are streaming video, each needing around 2-4 Mbps of upload bandwidth.
- General Use: All 10 employees are browsing the web, sending emails, and using other online services.
When you add it all up, the business needs a connection that can handle at least 10-15 Mbps of constant use, plus a healthy cushion for future expansion.
Step 4: Choose a Business-Grade Plan
For a business like this, symmetrical speeds and unwavering reliability are non-negotiable. A standard residential plan just won't do.
A business fiber plan, like Premier Broadband's 300 Mbps symmetrical service, would provide more than enough bandwidth. This ensures that call quality remains perfect even when multiple people are on the phone, designers are uploading huge files, and the security cameras are streaming. The final touch would be to implement QoS on their router to guarantee voice traffic always gets top priority.
Sample Bandwidth Calculation Scenarios
Here's a quick summary of how our two scenarios translate into real-world Premier Broadband plans.
| Scenario | Number of Users | Max Concurrent Calls | Estimated VoIP Bandwidth | Recommended Premier Plan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home Office | 1 | 1 | 0.1 Mbps | Premier Broadband 100 Mbps |
| Small Business | 10 | 4 | 0.4 Mbps | Premier Broadband 300 Mbps |
As you can see, the bandwidth needed just for VoIP is quite small. The key is choosing a plan with enough total capacity to handle everything else your home or business throws at it, ensuring your calls are always protected and clear.
Choosing The Right Internet For Flawless VoIP
When it all comes down to it, crystal-clear VoIP calls depend on more than just raw speed. You need a high-quality internet connection that delivers enough bandwidth—and delivers it consistently. Your entire VoIP system is only as good as the network it runs on, which makes picking your internet provider the most important decision you'll make for reliable communication.
Think of it like building a house. If the foundation is shaky, it doesn't matter how fancy the rest of the house is; it's always at risk. The same goes for your internet. Without a rock-solid connection, even the best VoIP phones will start to crackle and drop calls under pressure.
Why Fiber Is The Gold Standard For VoIP
The biggest enemies of a good VoIP call are jitter, latency, and packet loss. These are the network gremlins that turn a professional conversation into a choppy, robotic mess. A modern fiber internet connection is built from the ground up to fight these problems.
- Symmetrical Speeds: A voice call is a two-way street, and fiber gives you the same super-fast speeds for both uploads and downloads. This is non-negotiable for VoIP.
- Low Latency: Data travels over fiber-optic cables at the speed of light. This slashes the delay that causes people to accidentally talk over each other.
- Unwavering Reliability: Fiber is much less prone to weather or electrical interference, giving you a stable connection that keeps jitter and packet loss to a minimum.
Investing in the right internet isn't just a technical upgrade. It's an investment in the clarity and professionalism of every single conversation. It's the difference between frustration and communication that just works.
The world is rapidly moving to VoIP. In fact, over 40% of all voice calls globally are now made over VoIP networks, a number that’s growing 6% every year while traditional phone systems decline. This shift is powered by better internet that gives customers dependable connections for everything they do. That reliability means you won't have to worry about a call dropping in the middle of a storm or when everyone in the office is online.
Making Your Final Decision
The final step is to take a hard look at your current internet and see if it’s really up to the task. Does it offer the symmetrical speeds you need for clear back-and-forth calls? Is it stable enough to handle your busiest hours without dropping calls or introducing static?
If the answer is no, it’s time to talk to a provider who truly understands what VoIP needs to thrive. A good starting point is A Guide to VoIP Services in Canada for Businesses. By choosing a partner and a plan built for real-time communication, you’re setting your home or business up for success, one clear and dependable call at a time.
Got Questions About VoIP Bandwidth? We’ve Got Answers.
Even after you've done the math, a few questions about VoIP and bandwidth always seem to pop up. Let's clear up some of the most common ones we hear from people setting up their service for the first time.
How Much Speed Do I Really Need for One VoIP Call?
For a single, crystal-clear VoIP call, you'll need about 100 Kbps (or 0.1 Mbps) of dedicated bandwidth for both uploads and downloads. That number might seem tiny, but the secret is consistency. That sliver of bandwidth has to be available all the time, without getting hijacked by other things happening on your network.
That's why even a single home office user needs an internet plan with a lot more headroom. Think of it as a buffer. A plan with at least 10 Mbps of symmetrical speed is a great starting point to ensure your calls are always stable and professional.
Can I Get By with VoIP on a Slower Internet Connection?
Technically, yes, but your call quality will almost certainly take a hit. If you're stuck with a slow connection, your VoIP provider can sometimes switch you to a more data-efficient codec like G.729. This squeezes a call down to about 32 Kbps.
But this is a trade-off. Using a low-bandwidth codec often makes voices sound compressed or less natural. It’s an option in a pinch, but upgrading your internet connection is always the best long-term fix for professional-sounding calls.
Does Video Conferencing Use the Same Bandwidth as Voice Calls?
Not even close. Video is a completely different beast. While a voice-only call sips about 0.1 Mbps, a standard high-definition video call can guzzle 2-4 Mbps of both upload and download speed. If you’re in video meetings all day, you absolutely have to account for this much bigger number in your bandwidth budget to keep things running smoothly.
My Internet Is Fast, So Why Do My Calls Still Sound Awful?
This is a classic problem, and it proves that raw speed isn't everything. Even the fastest internet plans, particularly on older cable networks, can be plagued by quality issues that wreak havoc on VoIP:
- High Jitter: This is when data packets arrive all jumbled up, making voices sound choppy or robotic.
- Latency: You know that annoying delay where you end up talking over the other person? That's latency.
- Packet Loss: This is the worst of the bunch. Bits and pieces of the conversation just vanish into thin air.
The best way to fix this is by setting up Quality of Service (QoS) on your router. It essentially creates a VIP lane for your voice traffic, making sure your calls get first priority over everything else.
Ready to put an end to choppy calls for good? Premier Broadband delivers the symmetrical, high-speed fiber internet that VoIP systems demand to perform perfectly. Explore our internet and voice plans today and hear the difference a truly reliable connection makes.

