Before you can fix that frustrating lag, you have to play detective. The real problem usually isn't your raw internet speed—it’s a delay lurking somewhere in your local Wi-Fi, your router, or even further up the line with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Running a few simple diagnostics is the only way to find the culprit and apply the right fix.
Pinpointing the Real Cause of High Latency
Let's clear something up right away. High latency, or "lag," has very little to do with your download speed. It’s all about response time—the time it takes for a signal from your device to reach a server and come back, measured in milliseconds (ms). You can have a lightning-fast download speed, but if your latency is high, online gaming, video calls, and other real-time activities will feel sluggish and unresponsive.
Think of it this way: your bandwidth is like the number of lanes on a highway. Latency is the actual speed limit and traffic. You could have a ten-lane superhighway (high bandwidth), but if there's a massive traffic jam (high latency), getting from point A to point B is still going to be painfully slow. Our job is to find that traffic jam.
Starting Your Investigation
First, let's narrow things down. Is the lag hitting just one computer, or is every device on your network crawling? Does it only happen at night when the whole family is streaming movies? Answering these simple questions is the first step to zeroing in on the source of the problem.
Once you have a general idea, you can get more specific with diagnostic tools. These tools send tiny packets of data out to a server and time how long it takes them to return, giving you a clear, hard number for the delay. We cover how to use these in our guide on network diagnostic utilities, which will walk you through the process.
To get started, here’s a quick-glance table of the usual suspects when latency spikes.
Common Latency Culprits and Quick Fixes
| Potential Cause | What It Means | First Action to Take |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi Congestion | Too many devices are competing for airtime, or other networks are interfering with your signal. | Try switching to a less crowded Wi-Fi channel (like 1, 6, or 11 for 2.4 GHz) in your router settings. |
| Outdated Router | Your router's hardware or firmware can't keep up with modern internet demands. | Check the manufacturer's website for a firmware update. If it's over 5 years old, consider an upgrade. |
| Background Downloads | A device on your network is hogging all the bandwidth with large downloads or updates. | Check your connected devices for active downloads, cloud syncing (like Dropbox or OneDrive), or system updates. |
| ISP Peering/Routing | The path your ISP takes to connect to a specific game or service server is inefficient. | A traceroute test will show where the delay spikes. Sometimes a VPN can force a better route. |
| Local Network Hardware | A bad Ethernet cable, a faulty network switch, or a misconfigured device is causing the delay. | Test with a different Ethernet cable plugged directly into your modem to bypass other hardware. |
This table should help you quickly identify low-hanging fruit. By ruling out these common issues first, you can avoid a lot of headaches and focus your efforts where they’ll make the most impact.
Understanding the Tools of the Trade
You don’t need a networking degree to figure this out. A couple of simple, built-in commands are your best friends here.
- A ping test is your instant latency check. It measures the round-trip time to a specific server, giving you a direct reading in ms.
- A traceroute takes it a step further. It shows you every single "hop" your data makes on its journey and reveals how much delay is added at each point.
Traceroute is incredibly useful. If the first couple of hops show high ping times, the bottleneck is probably inside your own home—likely your router. But if the latency suddenly spikes several hops down the line, the issue is probably with your ISP's network or even further out on the internet.
This flowchart breaks down the process visually, helping you move step-by-step from your own gear to your provider.
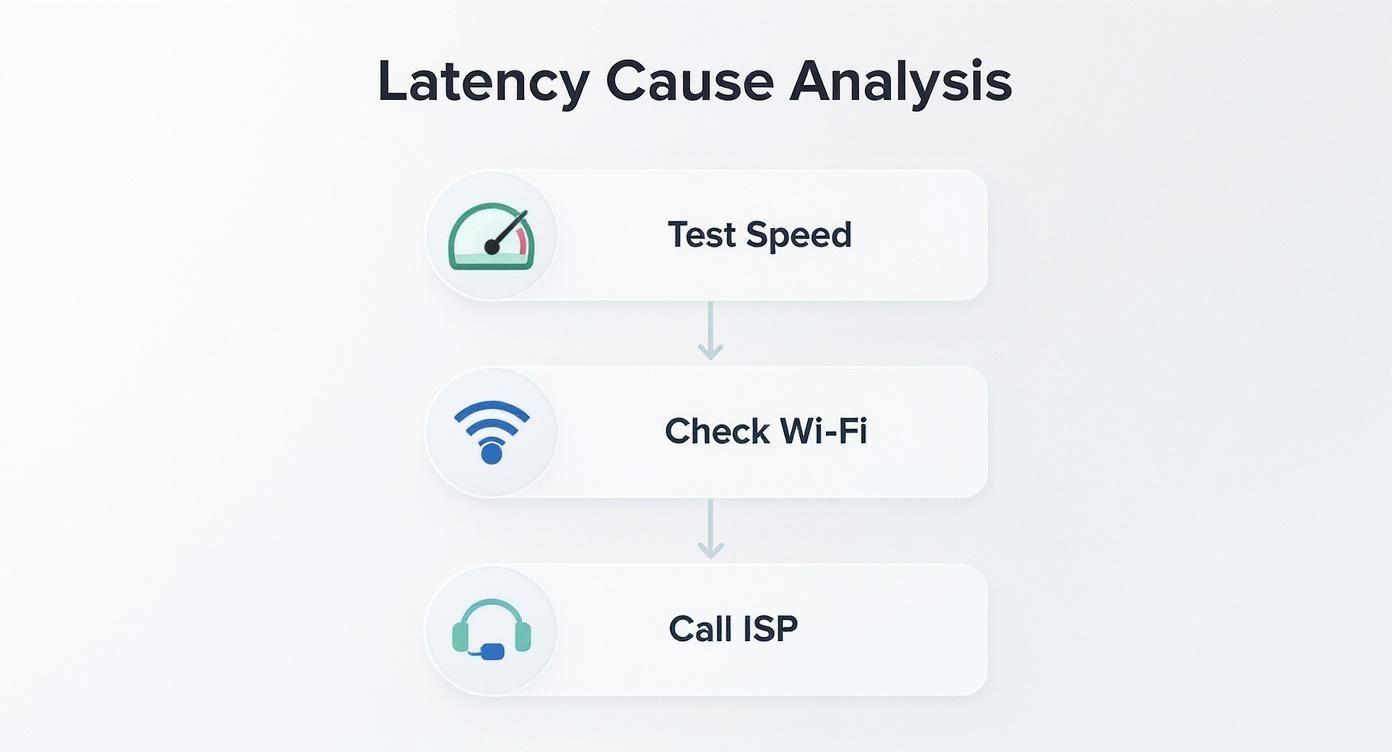
Following a logical path like this ensures you don’t waste time tweaking settings that aren't related to the actual problem.
For those who want to dig even deeper, it’s worth exploring some of the top network performance monitoring tools available. These can offer much more detailed insights than basic commands, helping you gather clear evidence before making any changes or calling for support.
Optimizing Your Home Wi-Fi Network

Alright, so you've tracked the latency problem to your own turf. Nine times out of ten, the Wi-Fi signal itself is the bottleneck. Wireless is great for convenience, but it’s also prone to all sorts of interference that can slam the brakes on your connection speeds.
We’re not just talking about rebooting your router here. These are specific, tactical adjustments inside your router's settings that can make a real difference, often without costing you a cent.
Taming Wi-Fi Interference with Channel Selection
Picture your Wi-Fi channels as lanes on a highway. When everyone—you and all your neighbors—is stuck in the same lane, you get a massive traffic jam. This is exactly what happens when everyone’s router is using the default channel (usually channel 6). This digital gridlock, called co-channel interference, is a huge source of lag.
Jump into your router’s admin settings and you can manually pick a new lane. For the 2.4 GHz band, which a lot of smart home gadgets use, your best bets are channels 1, 6, and 11. These are the only three that don't overlap, giving your signal the clearest path possible.
A quick change of channel forces your devices to reconnect on a less congested frequency. It’s a simple fix that can immediately cut down on those annoying ping spikes during gaming or video calls.
The Power of Separating Wi-Fi Bands
Most modern routers broadcast on two frequencies: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Often, they bundle these into a single network name, letting the router decide where to send your devices. This "band steering" sounds smart, but it's not always the best move for latency.
The 2.4 GHz band has better range but is slower and gets bogged down by everything from microwaves to cordless phones. On the other hand, the 5 GHz band is much faster and cleaner, though its range is shorter. For anything that needs a quick response, you absolutely want to be on 5 GHz.
You can take control by splitting the bands into two separate networks:
- MyNetwork_2.4GHz: Perfect for smart plugs, thermostats, and other devices that are far from the router and don't need blazing speed.
- MyNetwork_5GHz: Reserve this for your heavy hitters—gaming consoles, streaming devices, and work laptops—to get the lowest latency and best performance.
This move ensures your most important gear isn't getting shoved onto the slow, crowded 2.4 GHz highway. If you want to dive deeper into wireless performance, learning about choosing the right 5GHz Wi-Fi channel can help you fine-tune things even further.
Prioritizing Traffic with Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) is a game-changer hiding in your router's settings. Think of it as a bouncer for your network, deciding which data gets VIP access.
When you enable QoS, you can tell your router that your Zoom call is more important than a background download, or that your PS5 gets priority over a Netflix stream on another TV. This stops one bandwidth-hogging activity from creating lag for everyone else.
Most routers make this easy, letting you drag and drop devices into high, medium, or low priority groups. For anyone working from home or serious about online gaming, setting this up is a must. It’s how you get a stable, low-ping experience even when the whole house is online.
Modern Wi-Fi standards make features like QoS even more powerful. Check out our guide on Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6 technology to see how newer hardware can give you an even bigger performance boost.
Advanced Tweaks for Gaming and Streaming

So you've optimized your Wi-Fi channels and set up your QoS rules. That takes care of the biggest latency headaches for most people. But when every millisecond is the difference between winning and losing in an online match or keeping a 4K stream perfectly smooth, it's time to dig deeper. We're moving past the broad fixes and into the fine-tuning.
Let’s start with a simple truth: for anything that’s sensitive to latency, you can't beat a physical connection. No matter how great your router is, Wi-Fi will always be vulnerable to interference and signal drop-offs.
A wired Ethernet connection is your secret weapon. Plugging your gaming console, streaming device, or main work computer straight into the router gives you the most stable, low-latency link possible. It’s the gold standard for a reason.
Digging Into Device-Level Settings
Believe it or not, your computer's own network adapter has settings that can affect data processing. The default configurations are fine for everyday browsing, but a couple of small changes can shave off tiny delays that really add up.
If you’re a gamer looking for that competitive edge, check out the advanced properties of your network adapter for settings like these:
- Interrupt Moderation: Disabling this tells your CPU to process network data the instant it arrives, rather than grouping it into batches. It might bump up your CPU usage a little, but it's a fantastic trade-off for real-time responsiveness.
- Receive/Transmit Buffers: Playing with these buffer sizes can sometimes help, but you'll need to test it out. Smaller buffers can mean lower latency, but going too small might cause your system to drop data packets.
We're talking about micro-optimizations here, but when a 10-20 ms advantage matters, these settings become seriously powerful tools.
At the network level, even the way data is packaged and sent can introduce delays. Optimizing how applications serialize data and maintain connections can shave off critical milliseconds.
Studies have shown that efficient data formats can cut transmission overhead by 1 to 2 milliseconds for every 100 kB of data. For online games or financial trading platforms sending constant streams of information, those savings stack up fast. You can see the full study on optimizing latency-sensitive applications for a deeper dive.
The Role of Specialized Gaming Routers
While most modern routers get the job done, gaming routers are a different breed. They're built from the ground up to crush latency, often packing more powerful processors, extra RAM, and firmware designed to prioritize gaming traffic with laser focus.
These routers offer features you won't find on standard equipment:
- Geo-Filtering: This feature lets you block connections to game servers on the other side of the world, making sure you only play in lobbies with the lowest possible ping.
- Application-Specific Prioritization: Instead of just prioritizing your Xbox, these routers can identify the actual game data and give it an exclusive fast lane.
- Advanced Jitter and Packet Loss Reduction: They run specialized algorithms to smooth out the data flow, which is absolutely critical for clear voice chat and hiccup-free gameplay.
Getting the best internet for streaming and gaming is just one part of the equation. Pairing it with hardware built for the job is how you truly win. A gaming router is a specialized tool that guarantees your home network will never be the bottleneck holding you back.
When Hardware Upgrades Actually Make Sense
You've tweaked every software setting imaginable. You’ve optimized your Wi-Fi channels and even set up QoS to prioritize your gaming console. But the lag just won't quit.
When you've hit this point, you're no longer dealing with a simple configuration problem. You're running into the physical limits of your network hardware. Software can only do so much when your equipment is the real bottleneck.
If your router is a few years old, it's probably struggling to keep up with today's internet demands. Older wireless standards and slower processors just can't juggle the dozens of devices we have now. This is where a hardware upgrade becomes the most logical next step to finally fix high latency.

The Immediate Impact of a Wired Connection
Before spending a dime, try the simplest and most effective hardware upgrade of all: an Ethernet cable. A wired connection completely bypasses the interference, signal loss, and congestion that plague even the best Wi-Fi setups.
For any device that doesn't move—like a gaming PC, console, or your work-from-home desktop—plugging in directly should be your first move. It's a game-changer. The stability from a hardwired connection provides an instant and dramatic reduction in ping, often cutting latency in half compared to Wi-Fi.
Upgrading Your Router to Wi-Fi 6
If running cables everywhere isn't practical, your router is the next thing to look at. Upgrading from an older standard like Wi-Fi 5 to Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is about more than just speed; it's about efficiency.
Wi-Fi 6 was built for modern, crowded networks. It uses a technology called OFDMA that allows the router to talk to multiple devices at once, instead of making them wait in line. Think of it as a delivery truck that can drop off packages to several houses in one trip. This drastically cuts down the "waiting time" for each device, which directly lowers your latency.
Solving Coverage Gaps with a Mesh System
Sometimes the issue isn't your router's tech but its reach. In larger homes or buildings with thick walls, even a powerful router can leave you with dead zones where the signal is weak and unreliable. A weak signal means your devices are constantly re-sending data, which sends your latency through the roof.
This is exactly where a mesh Wi-Fi system shines. Instead of one central point of failure, a mesh system uses multiple nodes placed around your home to create one seamless, powerful network. Your devices automatically hop to the strongest signal, ensuring you always have a stable, low-latency connection no matter where you are.
Thinking about which hardware offers the best bang for your buck? This table breaks down how different upgrades typically impact latency.
Hardware Upgrade Impact on Latency
| Upgrade / Connection Type | Typical Latency Range | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Ethernet (Wired) | 1-10 ms | Gaming, video conferencing, and any stationary, mission-critical device. |
| Wi-Fi 6 Router | 10-30 ms | Homes with many smart devices and users competing for bandwidth. |
| Mesh Wi-Fi System | 15-40 ms | Larger homes or spaces with thick walls, brick, or multiple floors. |
| Fiber Optic Service | < 20 ms | The ultimate fix for low latency across all devices and applications. |
While these local network upgrades can make a huge difference, they are only one piece of the puzzle. The real leap in performance comes from the connection coming into your home.
Upgrading your local hardware is crucial, but the biggest leap in performance comes from the infrastructure delivering internet to your home. No router, no matter how powerful, can fix latency that originates outside your network.
The Ultimate Upgrade: Fiber Optic Internet
The single most impactful change you can make is switching to a fiber optic internet connection. Unlike cable or DSL that uses old copper wiring, fiber sends data as pulses of light through glass. It's just fundamentally faster and far more reliable.
Upgrading to fiber tackles latency at its very source. Global connectivity reports consistently show that infrastructure improvements lead to massive latency reductions. For example, recent data showed AT&T Fiber connections delivering latency as low as 18 ms, while T-Mobile's 5G network was at 45 ms. That's a 40-60% improvement over older technologies, proving that modern infrastructure is the key. You can find more details on how network upgrades impact latency performance.
If Premier Broadband's fiber service is available in your area, making the switch is the definitive way to fix high latency for good.
Dealing with Your Internet Service Provider
So, you've done everything on your end. You've tweaked your Wi-Fi, plugged your PC directly into the router, and fine-tuned every setting you can think of. But that frustrating lag just won't quit. When you've hit a wall troubleshooting inside your home, it's time to look at the source: your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Calling your ISP can feel like a chore, but going into the conversation with the right information can make all the difference. It's how you get past the standard "have you tried turning it off and on again?" script and get to someone who can actually solve your problem.
Come Prepared with Proof
Let's be honest, the first person you talk to in customer support has a script to follow. They have to ask you to reboot your modem. Your job is to show them you're way past that.
Before you dial, gather some hard evidence. Run a few speed and latency tests at different times of the day, especially when the lag is at its worst. It’s crucial to run these tests from a computer plugged directly into your modem via an Ethernet cable. This takes your Wi-Fi out of the equation completely.
Keep a simple log of your findings:
- Date and Time: Pinpoint exactly when you ran the tests.
- Download/Upload Speeds: Are they matching the plan you pay for?
- Latency (Ping): This is the key number. Note the ping time to a reliable server.
- Jitter and Packet Loss: If you see high jitter or any packet loss at all, that's a huge red flag pointing to an unstable connection.
When you can show a pattern of high latency even when your download speeds look fine, you have a powerful case. It proves you've done your homework and that this is a connection quality issue, not just "slow internet."
Talk Like a Pro
The words you use on the phone matter. If you say "my internet is slow," you're going to get the standard, basic troubleshooting script. You need to be more specific to get their attention.
Try framing it this way:
"I'm calling because I'm seeing consistently high latency and some packet loss, mostly during peak hours around 7 PM to 11 PM. My speed tests confirm I'm getting my advertised bandwidth, but my ping is jumping over 150ms. This makes gaming and video calls impossible. I've already confirmed this happens on multiple devices connected directly to the modem."
This kind of statement immediately shows you know what you're talking about. You've used key terms like high latency and packet loss, identified a timeframe (peak hours), and confirmed you've already isolated the problem from your own equipment. This pushes your ticket past the first level of support and toward someone who can look into the network itself.
Know When It’s Time to Move On
Sometimes, the issue isn't a technical glitch that can be fixed. It's a fundamental problem with your provider's network or the technology they're using.
Here are a few signs that it might be time for a bigger change:
- Nightly Slowdowns: If your connection quality tanks every single evening like clockwork, that's a classic sign of network congestion. It means your provider has too many customers in your area, and no amount of troubleshooting on your end will fix it.
- Painfully Slow Uploads: A lot of older cable and DSL plans have great download speeds but terrible upload speeds. In today's world of video calls, online gaming, and cloud storage, that slow upload can be a massive bottleneck.
- Outdated Tech: If you're still using DSL or an older cable connection, you're on last-generation technology. These copper-based networks just can't compete with the stability and low latency of modern fiber optics.
If your current provider can't solve the problem, it’s time to see what else is out there. Services like Premier Broadband that run on a 100% fiber network are often the ultimate solution. Switching to fiber is the single biggest upgrade you can make to permanently fix high latency. Fiber offers equally fast upload and download speeds and is naturally more stable, giving you the solid, fast connection that copper lines just can't deliver.
Common Questions About Fixing High Latency
Diving into network performance can be confusing when you're hit with a wall of technical terms. Let's cut through the jargon and get straight to the answers you need to solve high latency for good.
What Is a Good Ping Anyway?
What counts as a "good ping" really depends on what you're doing online. A ping that’s perfectly fine for browsing websites can make a competitive game totally unplayable. It’s all about context.
Here's a quick guide to understanding your ping results:
- Under 20 ms (Excellent): This is the sweet spot, the kind of performance you typically only see with a fiber optic connection. For competitive gamers, this is the goal.
- 20-50 ms (Great): Most online gaming and video calls will feel flawless in this range. Everything is smooth, responsive, and lag-free.
- 50-100 ms (Acceptable): This works for casual gaming and most work-from-home activities. You might notice a tiny delay, but it won't get in the way of what you're doing.
- Over 100 ms (Poor): Once your ping creeps over 100 ms, lag becomes obvious. Games feel sluggish, and you'll find yourself talking over people in meetings.
- Over 150 ms (Unplayable): At this point, real-time activities are just frustrating. The delay is so significant that it makes most online tasks a real chore.
Why Is My Latency High if My Download Speed Is Fast?
This is a classic problem. You're paying for a blazing-fast internet plan, and speed tests confirm you're getting massive download numbers, yet online games are still a laggy mess. The issue is the difference between bandwidth and latency.
Bandwidth (your download speed) is how much data you can move. Latency (your ping) is how fast that data makes a round trip. A big pipe doesn't mean the water flows faster.
Think of it this way: your download speed is the size of your car's trunk. A huge trunk (high bandwidth) lets you carry a lot of groceries at once. Latency is the time it takes you to drive to the store and back.
Even with a massive trunk, if the store is far away or you're stuck in traffic, the trip is still going to be slow. With your internet, high latency is often caused by physical distance to the server, congestion on your provider's network, or just bad routing—none of which are solved by a faster download package.
Can a VPN Help Fix High Latency?
Usually, no. In fact, a Virtual Private Network (VPN) almost always makes your latency worse. A VPN adds an extra stop for your data—it goes from your computer, to the VPN's server, then to its final destination. That extra hop naturally adds delay.
But there is one specific exception. Sometimes, your Internet Service Provider might be using a congested or inefficient path to connect you to a game server. A VPN can sometimes force your traffic onto a different, more direct route, bypassing that bottleneck.
This is rare, though. For the vast majority of people, the quickest way to lower your ping is simply to turn your VPN off while gaming or on video calls.
Tired of battling high latency on an old copper network? Premier Broadband delivers the ultimate fix with a 100% fiber optic connection, providing the ultra-low ping and symmetrical speeds you need for flawless gaming, streaming, and remote work. Upgrade to a connection built for performance today.

